Nursing Tips
Pediatric Nursing (78)

Spina Bifida Occulta
A child who presents with an abnormal tuft of hair, a dimple, or a birthmark on the spine should be evaluated for spina bifida occulta, a form of spina bifida....
Spina Bifida Occulta
A child who presents with an abnormal tuft of hair, a dimple, or a birthmark on the spine should be evaluated for spina bifida occulta, a form of spina bifida....

Absence Seizures: Signs and Symptoms
A child who appears to be frequently "day dreaming" or often exhibits blank staring, eye fluttering, lip smacking, or picking at clothes should be evaluated for absence seizures.
Absence Seizures: Signs and Symptoms
A child who appears to be frequently "day dreaming" or often exhibits blank staring, eye fluttering, lip smacking, or picking at clothes should be evaluated for absence seizures.

Acute Glomerulonephritis: Signs and Symptoms
A child demonstrating oliguria, cola-colored urine, and signs/symptoms of hypervolemia following a recent streptococcal infection (strep throat) should be evaluated for Acute Glomerulonephritis.
Acute Glomerulonephritis: Signs and Symptoms
A child demonstrating oliguria, cola-colored urine, and signs/symptoms of hypervolemia following a recent streptococcal infection (strep throat) should be evaluated for Acute Glomerulonephritis.

Key Symptoms of Coarctation of the Aorta
KEY symptoms of Coarctation of the Aorta: elevated BP and bounding pulses in the arms, decreased BP and pulses in the legs.
Key Symptoms of Coarctation of the Aorta
KEY symptoms of Coarctation of the Aorta: elevated BP and bounding pulses in the arms, decreased BP and pulses in the legs.

Key Symptoms of a Patent Ductus Arteriosus
KEY symptoms of a Patent Ductus Arteriosus: machine-hum murmur, bounding pulses, and wide pulse pressure.
Key Symptoms of a Patent Ductus Arteriosus
KEY symptoms of a Patent Ductus Arteriosus: machine-hum murmur, bounding pulses, and wide pulse pressure.

Signs and Symptoms of Autism
Key signs/symptoms of Autism: Lack of eye contact Repetitive motions/actions Delayed speech and language skills Strict adherence to routines Unusual eating or sleeping habits Digestive problems.
Signs and Symptoms of Autism
Key signs/symptoms of Autism: Lack of eye contact Repetitive motions/actions Delayed speech and language skills Strict adherence to routines Unusual eating or sleeping habits Digestive problems.
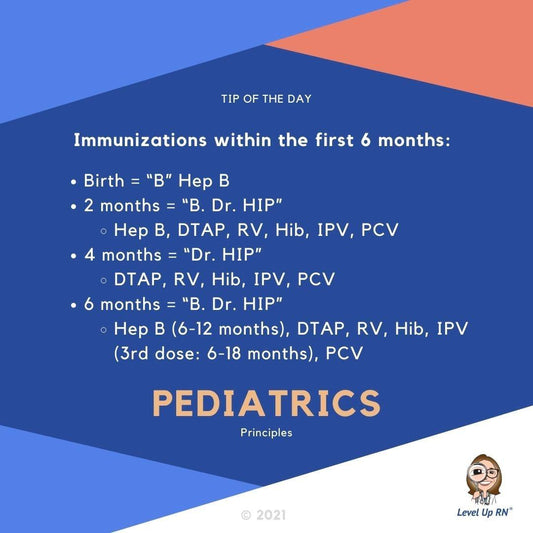
Immunizations in first 6 months
IMMUNIZATIONS IN FIRST 6 MONTHS Birth = "B" Hep B 2 Months = "B. Dr. HIP" Hep B, DTAP, RV, Hib, IPV, PCV 4 months = "Dr. HIP" DTAP, RV,...
Immunizations in first 6 months
IMMUNIZATIONS IN FIRST 6 MONTHS Birth = "B" Hep B 2 Months = "B. Dr. HIP" Hep B, DTAP, RV, Hib, IPV, PCV 4 months = "Dr. HIP" DTAP, RV,...

Parallel Play in Children
In toddlers, parallel play is expected. Parallel play means that children play independently NEXT to other children.
Parallel Play in Children
In toddlers, parallel play is expected. Parallel play means that children play independently NEXT to other children.

Severe Dehydration in Children
A child who is crying without producing tears should be evaluated for severe dehydration.
Severe Dehydration in Children
A child who is crying without producing tears should be evaluated for severe dehydration.

Injections for infants
For intramuscular injections under 1 year old, use vastus lateralis muscle!
Injections for infants
For intramuscular injections under 1 year old, use vastus lateralis muscle!

Giving Medication to Children
Educate families that when giving medication to children, they must use a calibrated device
Giving Medication to Children
Educate families that when giving medication to children, they must use a calibrated device

Early Signs of Increased ICP in Infants
Early signs of increased ICP in infants: irritability, high-pitched cry, poor feeding, “setting-sun” phenomenon, bulging fontanels, separation of cranial sutures.
Early Signs of Increased ICP in Infants
Early signs of increased ICP in infants: irritability, high-pitched cry, poor feeding, “setting-sun” phenomenon, bulging fontanels, separation of cranial sutures.

Crib Safety
Crib safety: Infants on back to sleep, nothing in crib, and width of crib slats
Crib Safety
Crib safety: Infants on back to sleep, nothing in crib, and width of crib slats

Key Beliefs of Preschoolers
2 Key beliefs of preschoolers: (1) Magical thinking: thoughts can cause events to occur, and (2) Animism: inanimate objects are alive.
Key Beliefs of Preschoolers
2 Key beliefs of preschoolers: (1) Magical thinking: thoughts can cause events to occur, and (2) Animism: inanimate objects are alive.

Infant weight gain
Infants should DOUBLE their birthweight by 6 months, and TRIPLE their birthweight by 1 year.
Infant weight gain
Infants should DOUBLE their birthweight by 6 months, and TRIPLE their birthweight by 1 year.

Indications of Bleeding After a Tonsillectomy
After a tonsillectomy, monitor for frequent swallowing or clearing of the throat. This can indicate bleeding at the incision site!
Indications of Bleeding After a Tonsillectomy
After a tonsillectomy, monitor for frequent swallowing or clearing of the throat. This can indicate bleeding at the incision site!
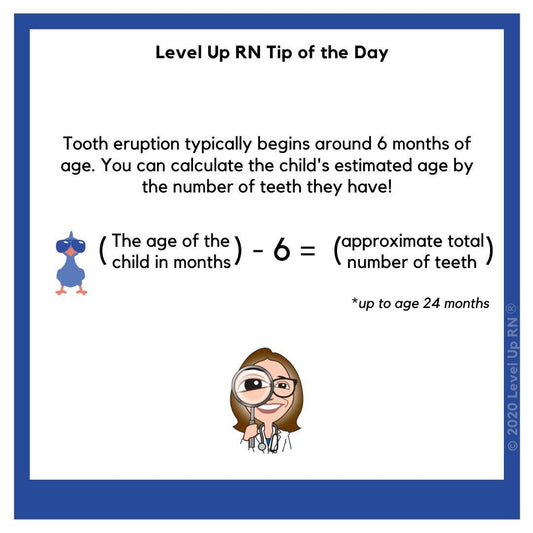
Tooth Eruption
Tooth eruption typically begins around 6 months of age. You can calculate the child's estimated age by the number of teeth they have!
Tooth Eruption
Tooth eruption typically begins around 6 months of age. You can calculate the child's estimated age by the number of teeth they have!
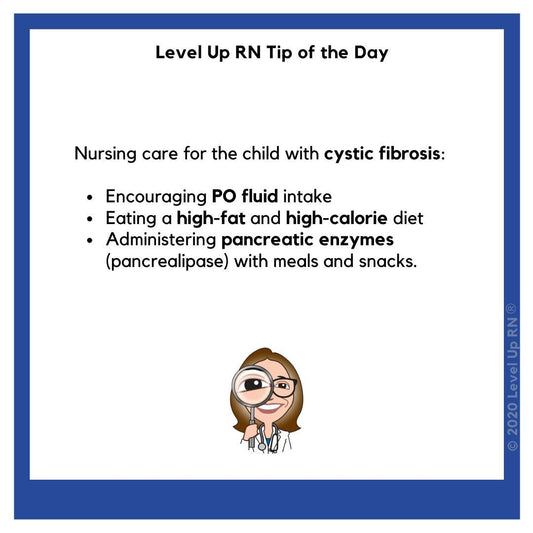
Cystic Fibrosis
Nursing care for the child with cystic fibrosis
Cystic Fibrosis
Nursing care for the child with cystic fibrosis
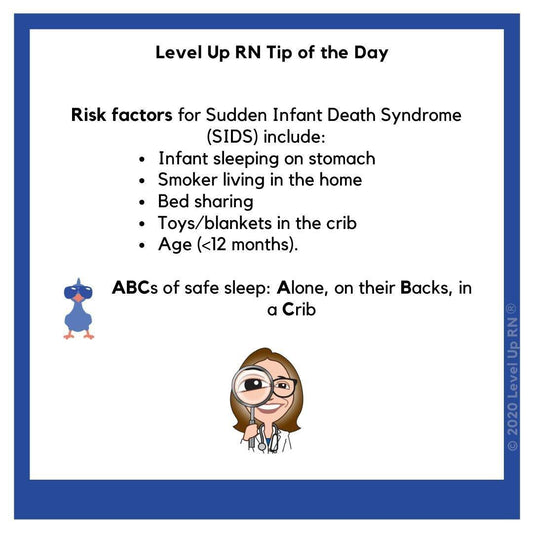
Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS)
Risk factors for Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS)
Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS)
Risk factors for Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS)
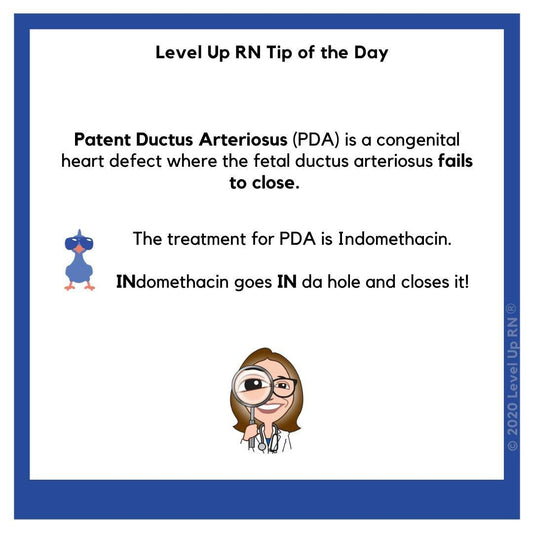
Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)
Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) is a congenital heart defect where the fetal ductus arteriosus fails to close.
Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)
Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) is a congenital heart defect where the fetal ductus arteriosus fails to close.

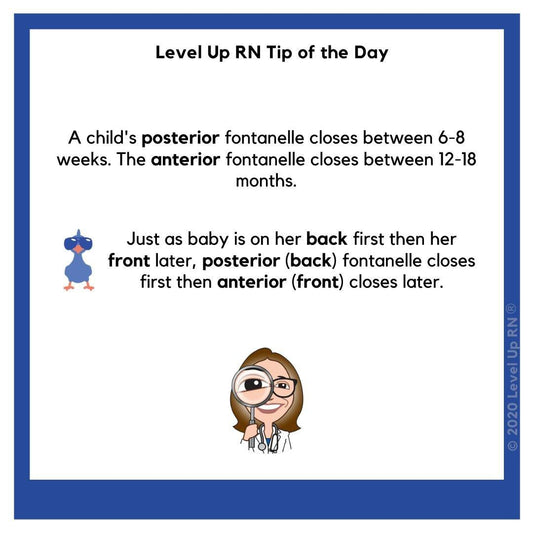
Fontanelle Closures
A child's posterior fontanelle closes first, then the anterior fontanelle closes.
Fontanelle Closures
A child's posterior fontanelle closes first, then the anterior fontanelle closes.
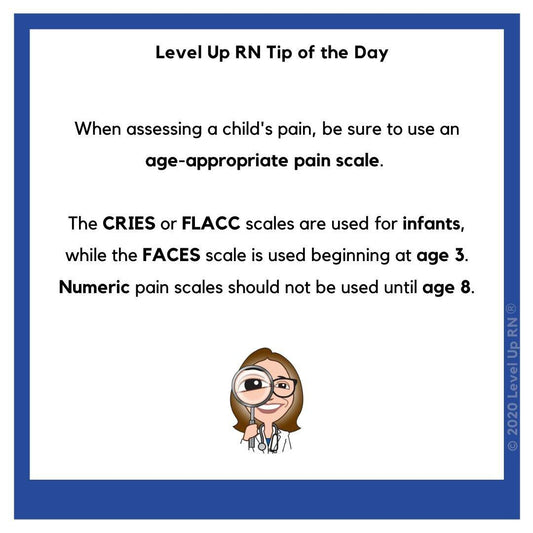
Pediatric Pain Scales
When assessing a child's pain, be sure to use an age-appropriate pain scale.
Pediatric Pain Scales
When assessing a child's pain, be sure to use an age-appropriate pain scale.

Signs of Physical Abuse
Signs of physical abuse. Always report ANY suspicion of abuse!
Signs of Physical Abuse
Signs of physical abuse. Always report ANY suspicion of abuse!
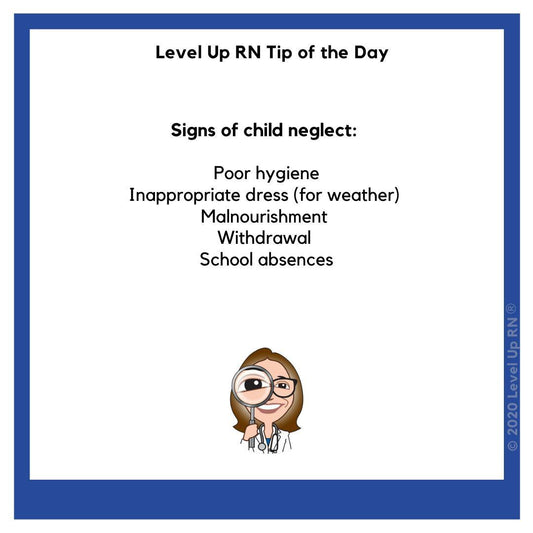
Signs of Child Neglect
Signs of child neglect: poor hygiene, inappropriate dress (for weather), malnourishment, withdrawal, school absences.
Signs of Child Neglect
Signs of child neglect: poor hygiene, inappropriate dress (for weather), malnourishment, withdrawal, school absences.
Major Risk Factor for Rheumatic Fever
Major risk factor for rheumatic fever: untreated or partially treated upper respiratory infection with Group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus (GABHS).
Major Risk Factor for Rheumatic Fever
Major risk factor for rheumatic fever: untreated or partially treated upper respiratory infection with Group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus (GABHS).

What to Do if You Suspect Epiglottitis
If you suspect that a patient has epiglottitis, DO NOT take a throat culture or place a tongue blade in the patient's mouth!
What to Do if You Suspect Epiglottitis
If you suspect that a patient has epiglottitis, DO NOT take a throat culture or place a tongue blade in the patient's mouth!

Major Risk Factor for Reye's Syndrome
Major risk factor for Reye's syndrome: Use of aspirin to treat fever associated with a viral infection.
Major Risk Factor for Reye's Syndrome
Major risk factor for Reye's syndrome: Use of aspirin to treat fever associated with a viral infection.

Signs of abuse in children
Signs of abuse in children: bruising in unusual locations (bruising on arms/legs expected!), bruising in different stages of healing, forearm spiral fractures.
Signs of abuse in children
Signs of abuse in children: bruising in unusual locations (bruising on arms/legs expected!), bruising in different stages of healing, forearm spiral fractures.

Choking hazard foods
The following foods pose a choking hazard for small children: popcorn, raisins, peanuts, grapes, raw carrots, hotdogs, celery, peanut butter, candy, tough meat.
Choking hazard foods
The following foods pose a choking hazard for small children: popcorn, raisins, peanuts, grapes, raw carrots, hotdogs, celery, peanut butter, candy, tough meat.
Filter Articles
Shop
The Ultimate Nursing School Survival Kit - with Flashables and Membership
4.875 / 5.0
(240) 240 total reviews
Regular price $349.95Regular priceUnit price / per$817.95Sale price $349.95SaleVideos by Subject
Tips & More
Exam Information
Subscribe


