Normal Albumin and Prealbumin Levels
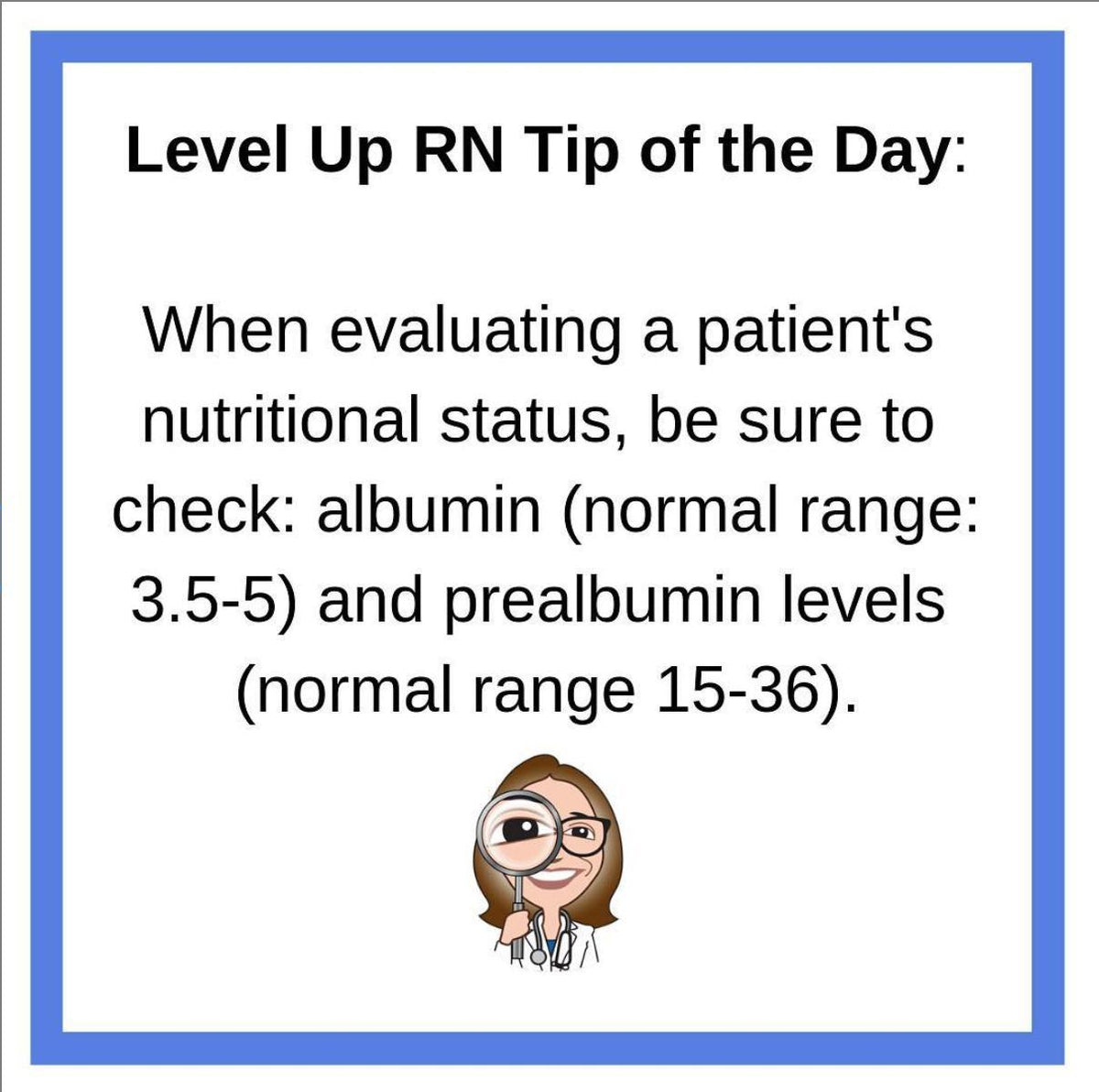
When you are evaluating a patient's nutritional status, you will need to check their albumin and prealbumin levels.
The normal range for albumin is 3.5 - 5 g/dL. Decreased levels of albumin can be caused by liver disease, kidney disease, or malnutrition. Low albumin levels can lead to edema, fatigue, and weakness.
The normal range for prealbumin is 15 - 36 mg/dL. Decreased levels of prealbumin are caused by protein-calorie malnutrition.
What is Albumin?
Albumin is a protein that is made in the liver and then found throughout plasma. It helps transport vitamins and nutrients throughout your body and keep fluids in your bloodstream. Having good amounts of albumin in the bloodstream is important to fight off infections, prevent muscle loss, and heal faster after surgery or illness.
What is Prealbumin?
Similar to albumin, prealbumin is a protein that is produced in the liver. The purpose of this protein is to help carry vitamin A and thyroid hormones throughout the body. This is also helpful because it allows your body to regulate how much energy it uses.
Prealbumin vs Albumin
Both prealbumin and albumin can be used to reflect the body's nutritional status, inflammatory state, and hepatic protein synthesis capabilities. Albumin levels are used more often than prealbumin in clinical practice. However, in some cases, prealbumin has proved to have higher specificity and sensitivity than albumin when evaluating protein malnutrition. Prealbumin also gives a more accurate picture of recent nutritional status in the immediate past, because it has a half-life of 2 days, while albumin has a half-life of 20 days.
What Does It Mean to Have High Albumin Levels?
High levels of albumin can indicate a variety of things, although it may not necessarily mean that a patient has a medical condition that needs treatment. When a test shows that there are higher levels of albumin it can indicate dehydration, severe diarrhea, or even other liver problems.
What is Albumin Used For?
Albumin injections are used for helping replace blood volume loss resulting from severe burns or other injuries that cause large blood loss. These injections are also helpful in treating hypoalbuminemia and low blood protein, and can help with acute liver failure.